Bile Duct Cancer
BILE DUCT CANCER (CHOLANGIOCARCINOMA)
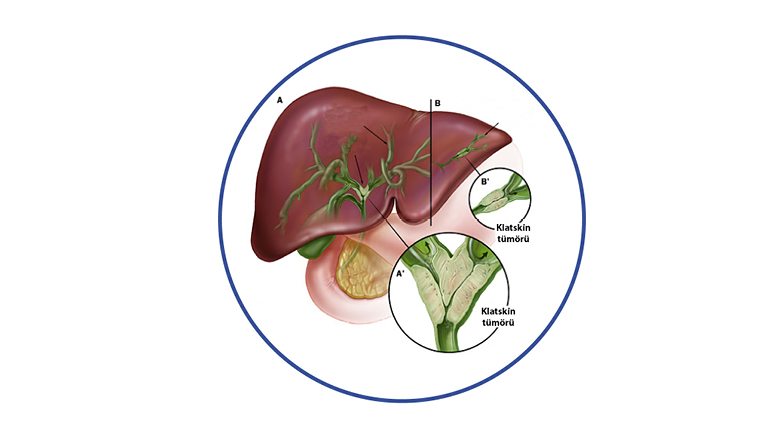
Cancer arising from the cells (epithelium) of the biliary tract. It can originate from any part of the biliary tree. It is called intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma if it originates from the biliary tract in the liver tissue, and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma if it originates from the biliary tract outside of the liver tissue. If extra-hepatic cholangiocarcinoma arises from the junction of the right and left biliary tract, it is called Perihilar biliary tract cancer (Klatskin tumor).
Symptoms
Jaundice is a presenting complaint in almost all cases of Klatskin tumors. Non-specific complaints, such as weight loss and abdominal pain, may also occur.
Diagnosis
Contrast enhanced spiral CT scanning provides highly accurate technique for imaging small lesions of biliary tree and clarifying the relationship of the tumor and portal venous and arterial structures. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is clearly identify the site and nature of biliary obstruction.
Surgery;
Surgery typically removes part of the liver, along with the bile duct, gallbladder, nearby lymph nodes, and sometimes part of the pancreas and small intestine. If there is an involvement of the hepatic artery and portal vein those are also can be resected and reconstructed in suitable patients. Then the surgeon connects the remaining ducts to the small intestine.
