Liver Cancer
WHAT IS LIVER CANCER?
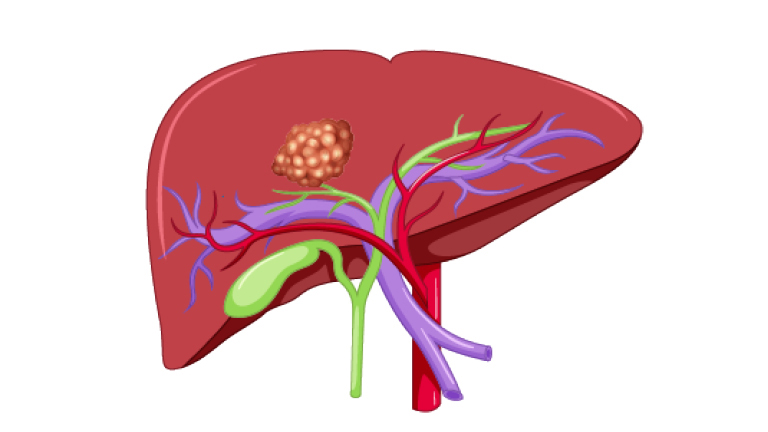
Liver cancer is the spread and growth of unhealthy cells in the liver.
1.METASTATIC LIVER CANCER

The spread of cancer in another organ of the body to the liver is called metastatic liver cancer. Most metastatic liver cancer are originating from colo-rectal cancers, additionally other cancers such as lung, stomach, breast, pancreatic cancer can also metastasize.
2.PRIMARY LIVER CANCERS

Cancers that start directly in the liver itself are called primary liver cancer (Hepatocellular cancer, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, hepatoblastoma etc.).
WHAT CAUSES HEPATOCELLULAR CANCER?
There are many reasons:
- Long-term presence of hepatitis B and hepatitis C can cause liver cancer. This may or may not be accompanied by cirrhosis.
- Excessive alcohol use
- Obesity (excessive weight) and diabetes cause a liver disease called non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, which increases the risk of liver cancer. This is even more common in people who also drink heavily or have viral hepatitis.
- Some inherited metabolic diseases
- Toxins exposed to environmental reasons such as aflatoxin
Hepatocellular cancer treatment depends on some factors:
- The condition of the liver
- Number, location and size of the tumor
- Whether it is in an organ other than the liver
- The patient's age and general health condition
HOW IS HEPATOCELLULAR CANCER TREATED?
If the cancer is limited to the liver that has not spread:
- Surgery; If the cancer is caught at an early stage and the remaining liver is healthy, the cancerous part of the liver can be surgically removed.
- Transplantation; If the liver is too bad to tolerate surgery, liver transplantation may be an option in suitable patients.
- Radio frequency ablation; The process of destroying cancer cells by applying heat with the help of a special probe (a needle inserted into the tumor tissue)
Other treatment options if surgery or liver transplant is not possible:
- Cryosurgery; process of freezing cancer cells using a metal probe
- Chemoembolization (TACE: Transarterial chemoembolization); to give anticancer drug from the blood vessel (chemotherapy) feeding the cancerous tissue and to block that vessel or to do this process without blocking it
- Radiation therapy; to damage cancer cells by giving radiation (high-energy x-ray) to the cancerous tissue in a very limited area
- TARE (Transarterial radioembolization therapy): It is often aimed to destroy cancer cells by injecting radioactive Yttrium-90 microspheres through the vessels feeding the cancerous tissue.
- Systemic treatments, immunotherapy
PRIMARY LIVER CANCERS
Cancers that start directly in the liver itself are called primary liver cancer (Hepatocellular cancer, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, hepatoblastoma etc.).
- Liver Hemangioma
It is the most common benign solid lesion of the liver. It is seen in 2-20% of the population. It is more common in women. The probability of spontaneous (spontaneous) bleeding is very low. Surgery is often only considered if it causes severe pain or decreases blood platelet levels. - Liver Adenoma
It is frequently seen in women using birth control pills. It can cause bleeding at a rate of 10-25%. Surgery is recommended as it has the potential to transform into a malignant tumor. - Fokal Nodüler Hiperplazi
Bayanlarda daha sık görülür. Şiddetli ağrıya neden olursa ameliyat önerilir. Onun dışında ameliyata gerek yoktur. - Local Nodular Hyperplasia
It is more common in women. Surgery is recommended if it causes severe pain. Other than that, there is no need for surgery
CYSTIC DİSEASES OF THE LIVER
- Cysts are the most common lesions in the liver.
- Congenital (congenital cysts)
- They are often simple cysts. It is seen in 5-14% of the society and is more common in women.
- Biliary cystadenoma
- Polycystic liver disease
- Caroli's disease
- Parasitic cysts (hydatid cyst etc.)