Bile Ducts Cancers
What is Bile Duct Cancer?
There are many small bile ducts inside the liver like the small branches of a tree. These ducts first form the right and left bile ducts at the lower edge and outside of the liver. These two channels join and become a single channel, then the gallbladder opens to itself and forms the main bile duct. The main bile duct opens into the duodenum and allows the bile produced in the liver to flow into the intestine. Cancer arising from bile duct cells it can originate from any part of the biliary tree, and the most effective treatment is surgery.
Do Gallbladder Polyps Cause Cancer?
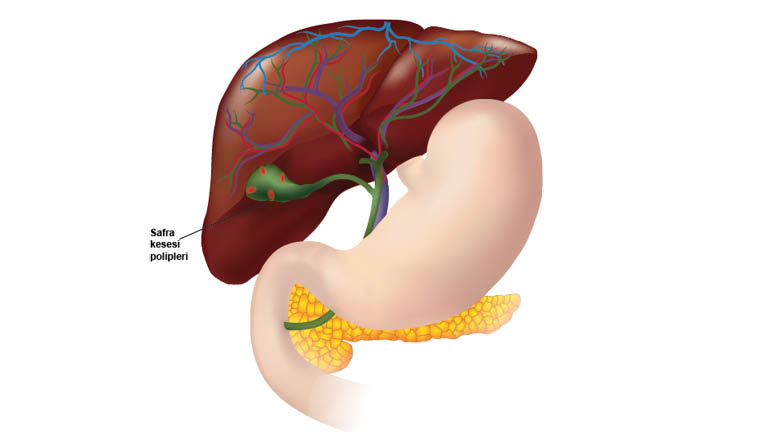
Gallbladder polyps are formations that originate from the inner surface of the gallbladder and extend into the gallbladder. About 95% of gallbladder polyps are benign and rarely turn into cancer. The size of a gallbladder polyp can help predict whether it is cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign). Gallbladder polyps smaller than 5 mm in diameter do not require any intervention. Regular control is important for polyps between 5 and 10 mm in size. However, gallbladder polyps larger than 10 mm are more likely to be cancerous or turn into cancer over time, and in this case, surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) is recommended. If you have gallbladder polyps of any size accompanied by gallstones, your doctor may also recommend cholecystectom
Gallbladder Cancer Surgical Methods
Cancers originating from the gallbladder are called gallbladder cancer. Unfortunately, most progress quickly. While some patients apply with complaints such as jaundice, abdominal pain, and palpable mass, some patients learn about their disease incidentally when a pathology report comes out as a result of a gallbladder surgery due to gallstones.
While a simple gallbladder surgery may be sufficient according to the stage of the tumor, a complex surgery may also be required that makes it necessary to clean the lymph nodes including the liver and biliary tract.
Importance of Surgeon's Experience in Klatskin Tumor

The Klatskin tumor, also called perihilar cholangiocarcinoma, is located at the junction of the right and left bile duct. Only 50% of the patients can be operated because it is in close proximity with the vessels that feed the liver and it sometimes requires vascular surgery and remove most of the liver in its operation. The equipment of the center and the experience of the surgeon are very important in this disease in which only one out of every two patients can be operated on.
