Liver Cancer
What Is Liver Cancer?

Liver cancer is the growth and spread of unhealthy cells in the liver. Cancer that starts in the liver is called primary liver cancer. Cancer that spreads to the liver from another organ is called metastatic liver cancer. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer. Cancer from colorectal origin is the most common type of metastatic liver cancer.
What Are Liver Cysts? How Does It Occur?
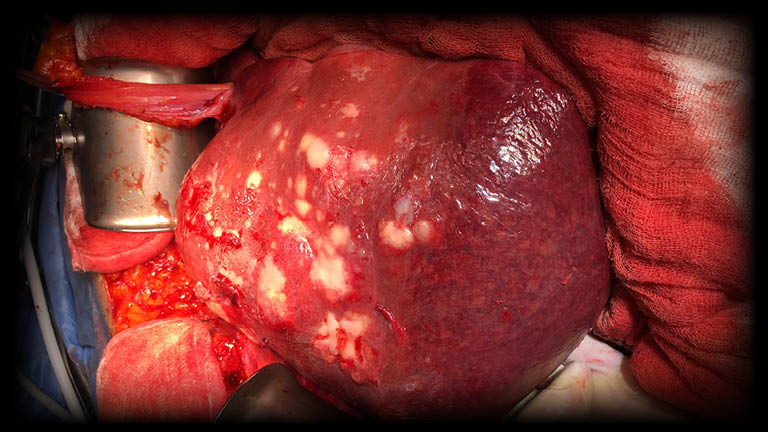
Liver cysts are one of the cysts that occur in the form of fluid-filled sacs in the liver and can be seen in many people. Often it is difficult to see the symptoms right away. However, these cysts can be diagnosed with various imaging techniques. Although some of them are benign, malignant cysts are frequently encountered. In particular, early treatment of malignant cysts is important in terms of preventing the disease from progressing. Among the types of liver cysts; Echinococcosis, simple cysts and cystadenomas can be listed. However, liver cysts can also cause polycystic liver disease.
Who Is At Risk For Liver Cancer?
Liver cancer is caused by an unhealthy lifestyle, as well as breast, bladder, kidney, ovarian, uterine and skin cancers that can frequently metastasize to the liver. There are also some factors known to increase the risk of developing liver cancer, including:
- Liver cancer is more common in people over age 50.
- A long-term hepatitis B or C infection can severely damage your liver.
- Having two or more alcoholic beverages every day over many years increases your risk for liver cancer.
- Cirrhosis is a form of liver damage in which healthy tissue is replaced by scarred tissue. A scarred liver can’t function properly and may ultimately lead to numerous complications, including liver cancer.
- Exposure to aflatoxin is a risk factor. Aflatoxin is a toxic substance produced by a type of mold that can grow on peanuts, grains, and corn.
- Diabetes and obesity are also risk factors. People with diabetes tend to be overweight or obese, which can cause liver problems and increase risk for liver cancer.
How Is Liver Cancer Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of liver cancer begins with a medical history and a physical examination. Make sure to tell your doctor if you have a history of long-term alcohol abuse or a chronic hepatitis B or C infection. Diagnostic tests and procedures for liver cancer include the following:
- Liver function tests help your doctor determine the health of your liver by measuring levels of proteins, liver enzymes, and bilirubin in your blood.
- The presence of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in the blood can be a sign of liver cancer.
- Abdominal CT veya MRI scans produce detailed images of the liver and other organs in the abdomen. They can allow your doctor to pinpoint where a tumor is developing, determine its size, and assess whether it has spread to other organs.
- Liver biopsy, another diagnostic test available is a liver biopsy. A liver biopsy involves removing a small piece of liver tissue.
How Is Liver Cancer Treated? What Are The Treatment Methods?
Surgery is the most effective treatment for liver cancer. Among the factors that affect the decision of surgery, we can count the size and number of the tumor, its relationship with the vessels, whether there is damage to the normal liver tissue due to long-term chemotherapy. In hepatocellular cancer the degree of accompanying cirrhosis is another important issue that should have to take into account. Liver transplantation can be an only choice for some hepatocellular cancer patients.
In patients who are not suitable for surgery, with injection of certain substances into the tumor tissue with a needle and/or radiofrequency waves may be possible to destroy or reduce the tumor mass. Although chemotherapy and chemoembolization are other treatment methods that can be applied, radioembolization is another method that can be applied together by nuclear medicine physicians and interventional radiologists.
How Should Nutrition Be In Liver Cancer!

In liver cancer, a balanced diet supports healing and supports your general health. It is important to get enough calories and nutrients. It is important to eat a balanced diet that includes plenty of fiber-rich foods to support liver function. Liver cancer symptoms and side effects of some treatments can affect your ability to eat. For example, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting or diarrhea may develop. Drinking water is very important, especially if you are experiencing vomiting, diarrhea or constipation.
How Does Liver Cyst Occur?

Liver cysts can be congenital, usually from our pets (such as dogs), parasites that enter the body by transmitting to human intermediate hosts, easily cross the intestinal wall, reach the liver by using blood and lymph and cause cysts. Apart from this, they also settle in the lungs and all other organs and continue their lives as cysts. Since they are very small in the first time they enter the body, they do not show themselves much. However, cysts start to grow over time and cause various pressures in the area where it is located. This situation exposes people to various risks.
What Are The Symptoms Of Liver Cyst?
In the initial period, liver cysts may not cause any obvious complaints. However, over time, when the cyst grows and starts to take a place for itself, some symptoms begin to appear. The most common symptoms are:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Digestive problems
- Obstruction, jaundice and infection in the bile ducts
- Severe and persistent abdominal pain
What Is Liver Metastasis?
The liver is a large organ that filters the blood. Therefore, cancer cells that enter the bloodstream remain stuck in this organ and continue to grow. Especially since the blood coming from the digestive system (large intestines) first passes through the liver, liver metastases of cancers belonging to these organs are more common. Liver metastases are common in cancers of organs such as the large intestine, stomach, pancreas, biliary tract, and small intestine. Metastases from breast cancer, lung cancer and lymphoma are also common.
Metastatic Liver Tumors
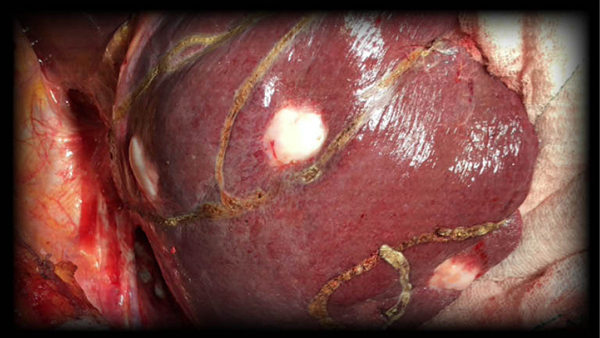
Metastatic cancer means the spread of the cancer from its origin organ (primary focus) to another region or organ (secondary area) in the body. When we say metastatic liver cancer, it is understood that a cancer originating from other organs often spreads to the liver usually through the blood.
Cancers that most frequently metastasize to the liver; large intestine (colon-rectum), breast, bladder, kidney, ovary, pancreas, stomach, uterus, and lungs. Among these, the most common metastatic liver cancers are those originating from the large intestine.
What Are The Symptoms Of Liver Cancer?
Liver cancer often does not manifest itself. However, as it grows, it can cause pain in the upper abdomen, back or shoulder on the right side, a feeling of fullness and bloating.
Fatigue, nausea, loss of appetite, weight loss, weakness, fever and jaundice (yellowing of the eyes and skin), swelling of the legs (edema) may occur.
Do Patients With Metastasis Have A Chance Of Surgery?
Although it varies according to the type of cancer, surgery may not be the main treatment method in every patient with metastasis. However, surgical removal of metastases in some cancers provides a significant survival advantage to the patient. For example, patients live longer when liver metastases from colon cancers are removed. For this reason, it is very important to treat cancer patients in the right centers where surgeons and oncologists work in harmony.
What Are The First Symptoms Of Liver Cancer?
Many patients with liver cancer do not have any early symptoms. Therefore, even if there are no complaints, especially in high-risk patients such as cirrhosis, follow-up is very important for early diagnosis. Liver cancers usually cause bloating in the abdomen, yellowing of the skin, itching, pain starting from the right upper part of the abdomen to the back, sudden weight loss, loss of appetite, feeling of fullness and bloating after a meal despite eating very little, fever, sweating at night, sudden worsening in general health,. It is manifested by signs of jaundice such as pale stools and darkening in the color of urine.
What Are Liver Cysts? How Does It Occur?
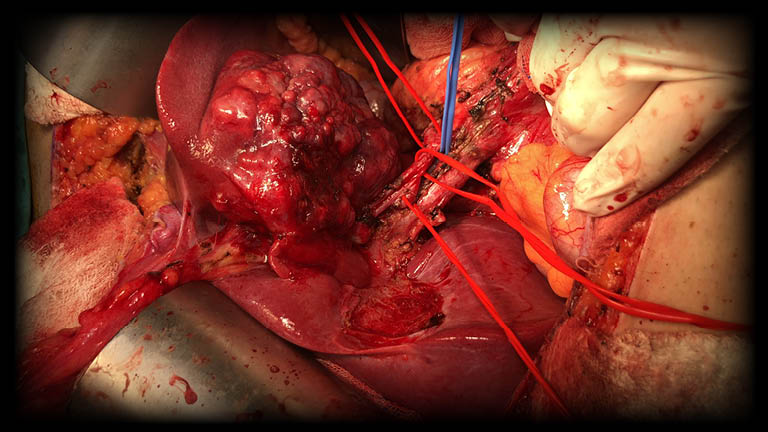
Liver cysts are one of the cysts that occur in the form of fluid-filled sacs in the liver and can be seen in many people. Often it is difficult to see the symptoms right away. However, these cysts can be diagnosed with various imaging techniques. Although some of them are benign, malignant cysts are frequently encountered. In particular, early treatment of malignant cysts is important in terms of preventing the disease from progressing. Among the types of liver cysts; Echinococcosis, simple cysts and cystadenomas can be listed. However, liver cysts can also cause polycystic liver disease.
How Is Liver Cancer Diagnosed?
Although the chance of early diagnosis is low in liver cancer; periodic examinations and blood tests are especially important in patients with known cirrhosis and cancer in a different part of the body. In order to confirm the presence of liver cancer, your doctor may request blood tests and imaging such as ultrasonography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and may require biopsy if necessary.
What Is Hepatocellular Carcinoma?
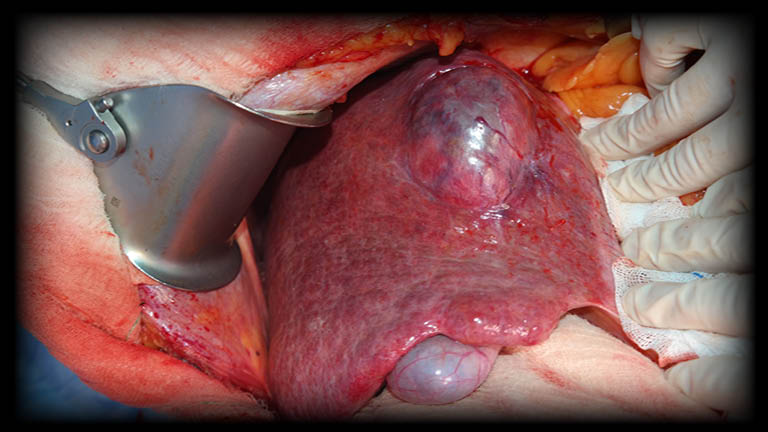
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary malignant tumor of the liver originating from hepatocytes. The biggest risk factor of hepatocellular carcinoma is cirrhosis. The most common causes of cirrhosis in our country are viral hepatitis (HBV, HCV) and alcohol. Apart from these, other factors that increase the risk of hepatoma; male gender, nonalcoholic fatty liver, diabetes, and smoking. Cancer is the second most common cause of death worldwide, and liver cancer is the second most common cause of cancer deaths.
What Causes Hepatocellular Cancer?
It is one of the primary cancers of the liver. It develops in most patients in the presence of a chronic (long-standing) liver disease. There are many reasons:
- Long-term presence of hepatitis B and hepatitis C. This may or may not be accompanied by cirrhosis.
- Excessive alcohol use
- Obesity (overweight) and diabetes (diabetes); causes a disease called non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (steatohepatitis) in the liver, this disease increases the risk of liver cancer. This is even more common in people who also drink heavily or have viral hepatitis.
- Some inherited metabolic diseases (eg, hemochromatosis disease, which increases the iron content in the blood)
- Lifestyle and dietary habits, Toxins which are frequently encountered in dried foods such as aflatoxin.
If The Tumor Is Adjacent To The Liver Vessels?
If the tumor is adjacent to the liver vessels? There are 2 main vessels that bring blood to the liver and 3 main vessels that direct this blood towards the heart after feeding the liver. These veins are vital for liver health, so they should be protected as much as possible during cancer surgery. The surgeon's experience, the techniques used, and the use of ultrasonography are very important to remove cancerous tissue without leaving cancerous tissue behind and at the same time without damaging the vein.
What Does Cholangiocarcinoma Mean?
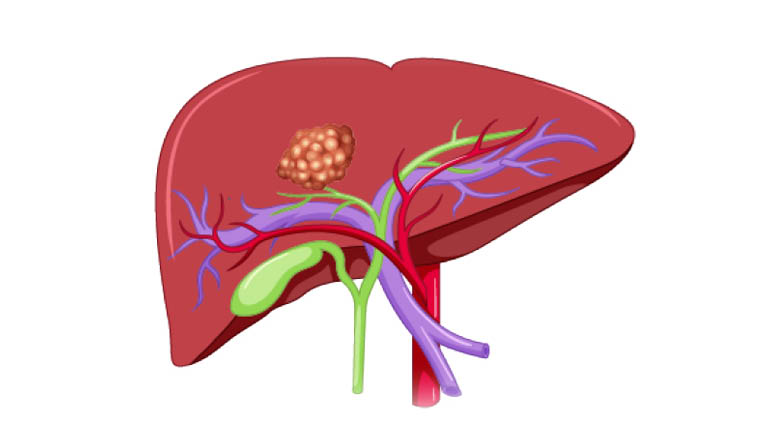
Cholangiocarcinoma is cancer that forms in the bile ducts that carry the digestive fluid bile. Bile ducts connect your liver to your gallbladder and to your small intestine. This condition, also known as bile duct cancer, is an uncommon form of cancer that occurs mostly in people older than age 50, though it can occur at any age.
Cholangiocarcinoma divide into different types based on where the cancer occurs in the bile ducts:
- Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma occurs in the parts of the bile ducts within the liver
- Hilar cholangiocarcinoma occurs in the bile ducts just outside of the liver. This type is also called perihilar cholangiocarcinoma.
- Distal cholangiocarcinoma occurs in the portion of the bile duct nearest the small intestine.
- Complete surgical resection is the only therapy to afford a chance of cure for cholangiocarcinoma. Unfortunately, many patients present with unresectable disease.
What Is Radiofrequency Ablation (Rfa)?
In liver cancer, surgical removal of the tumor should be the main goal. However, in patients whose general condition is too weak and risky to be operated on, or sometimes in additional lesions that cannot be surgically removed during surgery, the process of damaging tumor tissues with radiofrequency waves applied through a needle inserted into the tumor is called radiofrequency ablation.
What Is Liver Resection And Lobectomy?
In liver cancer, the amount of liver tissue to be taken is decided according to the number, size and extent of the tumor. Resection is the general name given to the removal of liver tissue. The liver consists of two lobes, right and left. Lobectomy is the removal of one of the two main parts of the liver. This surgery is performed in patients with cancer large enough to cover the entire lobe.
